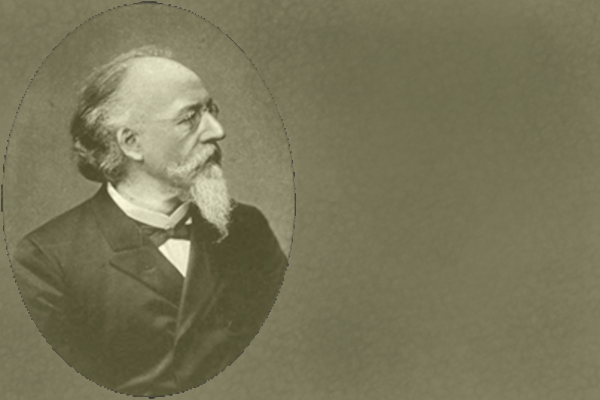The Faculty for Chemistry and Pharmacy
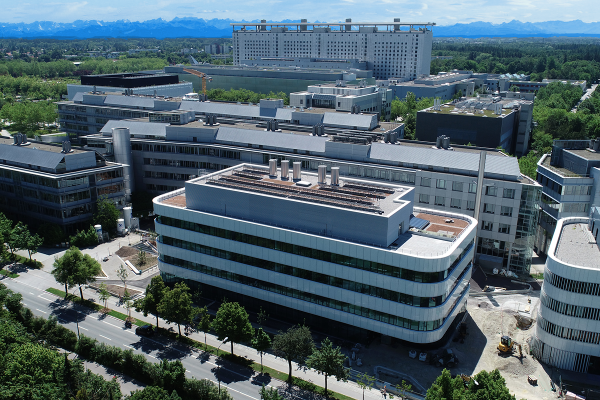
The Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy at LMU Munich is one of the best in its field. It is part of the Grosshadern/Martinsried campus, a unique cluster of research institutions in the natural and life sciences in Europe - from discovery to application.
About us
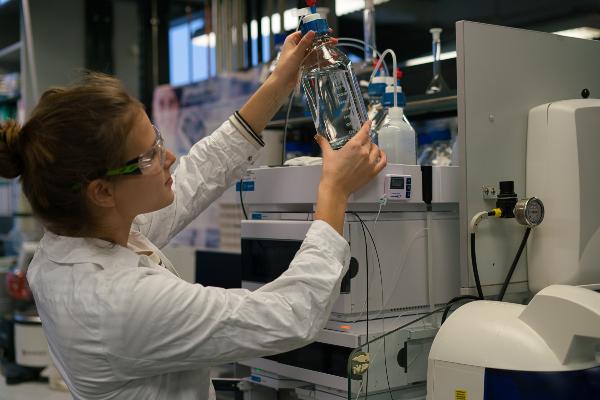
Our faculty is located on the Campus Großhadern/Martinsried in Munich's Großhadern district. It has a rich history and has stood for excellent research and teaching for several hundred years. In our three departments biochemistry, chemistry and pharmacy we conduct research into many relevant questions of the present and aim to make our contribution for a better society and future.
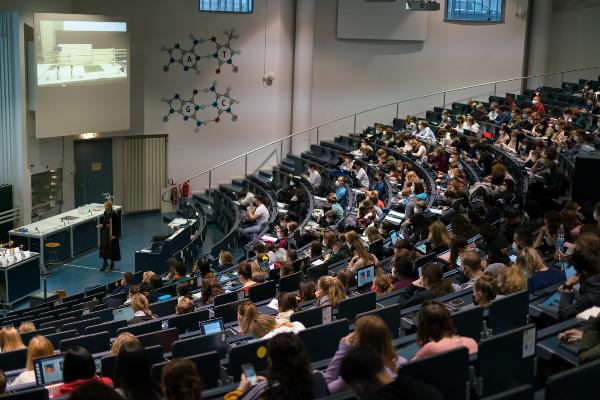
In teaching, we have always taken new, forward-looking paths. Recently, this has included the establishment of contemporary and needs-oriented new courses of study such as "Pharmaceutical Sciences" the international, English-language Master's in Biochemistry and the Bachelor's and Master's in Chemistry.
In addition to the many publications in excellent international journals and numerous innovative patents of our research groups, our research successes include the founding of the Cluster of Excellence "Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM), the Graduate School of Excellence “Quantitative Biosciences Munich” (QBM), the Cluster of Excellence “E-Conversion” (e-conversion, together with the Technical University of Munich), the future cluster “Cluster for Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Munich” (CNATM) and other Collaborative Research Centers. In addition to our numerous programs in basic research, biotechnology companies are also involved in order to make the Munich region a globally visible melting pot for innovation, progress and teaching in the field of life sciences.
The faculty was a pioneer in establishing the tenure-track system to appoint young researchers to a professorship directly after their post-doctoral period and thus compete with the Anglo-Saxon system for the best talent. In addition, the faculty was one of the first in Germany to proactively initiate appointments in order to bring outstanding researchers from the USA back to Germany.
Members of the faculty have also received many internationally acclaimed awards. For example, six faculty members have been awarded prizes in the Leibniz Program of the German Research Foundation (DFG). Around 30 faculty members have received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) to date. In addition to other programs, the DFG-funded Collaborative Research Centres have kept the third-party funding ratio high.
Every year, the Römer Foundation honors the best graduates and researchers in the Departments of Chemistry and Biochemistry at a graduation ceremony.
History of our Faculty
1472
Foundation
Duke Ludwig IX, also known as Duke of Bavaria and Louis the Rich, founds the first "high school" in Bavaria, situated in Ingolstadt: The Ludwig Maximilians University of Munich (LMU) one of the Germany's oldest universities. Learn more
1800
Relocation
Prince-Elector Max IV Joseph of Bavaria (later on King Maximiliam the I) relocated the "high school" to Landshut. Learn more
1818
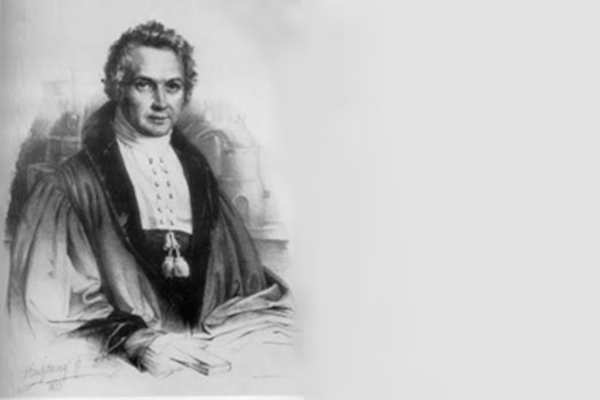
Johann Andreas Buchner, a Munich pharmacist, is appointed professor for pharmacy and pharmacology at the "high school" in Landshut. Learn more
1826
King Ludwig I of Bavaria orders the relocation of the university (which was later on named after Dutch Ludwig the Rich and King Maximilian I) from Landshut to Munich. Learn more
1852
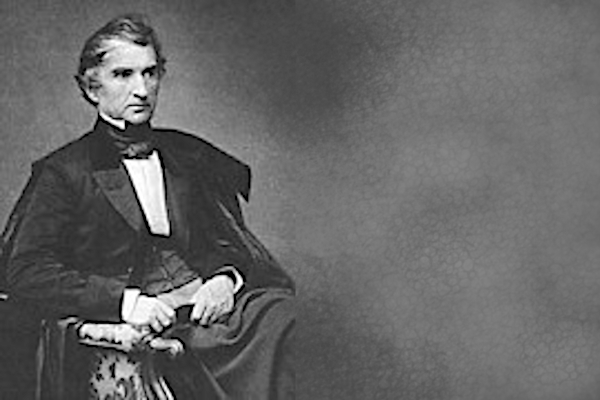
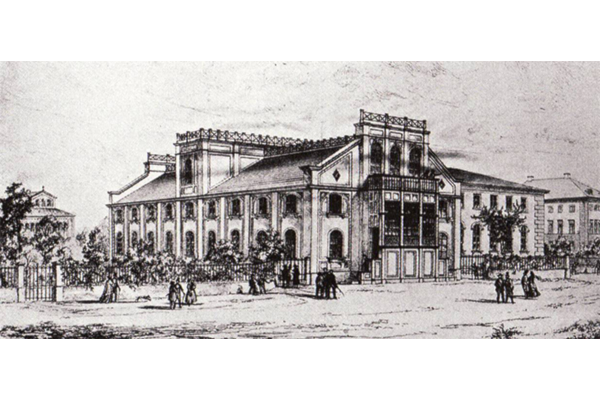
Justus von Liebig, who was the most famous chemist at that time and who was formerly professor in Gießen, is appointed for the professorship of chemistry and receives a new building in the Sophienstraße and Arcisstaße. Among his doctoral students where to name a few: Friedrich August Kekule von Stradonitz, August Wilhelm von Hofmann, Emil Erlenmeyer and Adolph Strecker. Learn more
1870
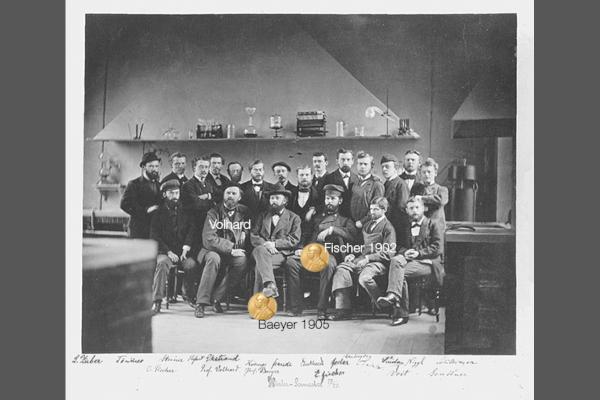
The "Chemical Laboratory" under the direction of Adolf von Baeyer.
1875
Nobel Prize for Chemistry
Two years after the death of Liebig, Adolf von Baeyer is appointed full professor of chemistry. The institute, which receives in addition to the organic department an inorganic department, becomes the best known school for chemistry in Germany after an expansion under Baeyers management. In 1885 Baeyer is ennobled and in 1905 he receives the Nobel Prize for Chemistry for research about organic dyestuffs. Learn more
1877
To Baeyers working group belong a lot of students who later on were honored as eminent scientists, for example: Emil Fischer (Nobel Prize Laureate in Chemistry 1902), Eduard Buchner (Nobel Prize Laureate in Chemistry 1907), Richard Willstätter (Nobel Prize Laureate in Chemistry 1915) and Heinrich Wieland (Nobel Prize Laureate in Chemistry 1927).
1892
Albert Hilger
Chemistry and Pharmacy are shifted from the medical to the philosophical faculty. Albert Hilger from Erlangen, is appointed for the professorship for pharmaceutical chemistry and receives a new building for the institute in the Karlstraße. In 1894 an "Anstalt for Nahrungs- und Genussmittel" (institute for food and stimulates) is affiliated. Learn more
1893
Group picture of the members of the chemical institute. Besides the two Nobel Prize laureates Baeyer and Willstätter are pictured: Walter Dieckmann ("Dieckmann Condensation"), Johannes Thiele ("Thiele Hypothesis of Partial Valencies") and Victor Villiger ("Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation").
1905
Adolf von Baeyer receives the Nobel Prize fo Chemistry. Theodor Paul, student of Wilhelm Ostwald, overtakes the professorship for pharmaceutical chemistry. In 1916 a "Gerichtlich-Chemische Untersuchungsstelle"(judicial-chemical investigation department) and "Forschungsanstalt für Lebensmittelchemie" (research institute for food chemistry) are established.
1915
A. v. Baeyer resigns. Richard Willstätter, a student of Baeyer and head of the Kaiser-Willhelm-Institute for Chemistry in Berlin, is appointed full professor of chemistry of the "Chemical Laboratory of the State". In the same year, Willstätter receives the Nobel Prize for Chemistry 1915 for research about vegetable dyes. The chemical institute is extended and modernized. Learn more
1926
Heinrich Wieland becomes Willstätters successor. He is a student of Baeyer and head of the chemical institute in Freiburg. In 1927 Wieland receives the Nobel Prize for Chemistry because of his research about bile acids. Learn more
1932
Kasimir Fajans, born in Warshaw, becomes head of the Institute of Physical Chemistry at the Sophienstraße, which was built with the aid of the Rockefeller Foundation. As he is Jewish, he is dismissed and denaturalized in 1936. Learn more
1935
A pharmacognostic instiute ("Institute for pharmaceutical pharmacology”) is established in the Karlstraße.
1950
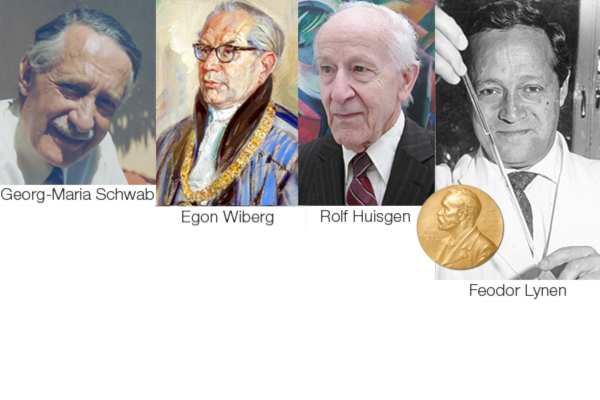
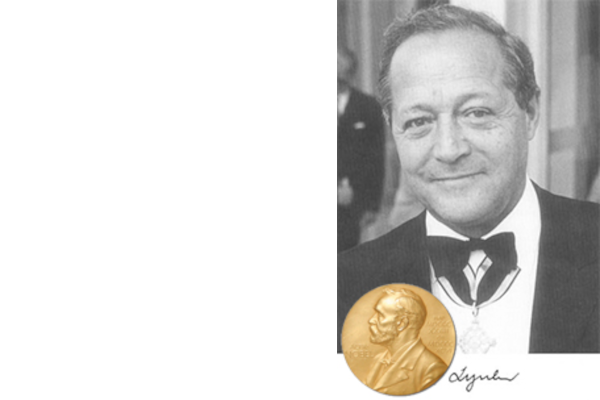
Heinrich Wieland is given emeritus status. Until 1953, four professorships are established and staffed: Georg-Maria Schwab (physical chemistry), Egon Wiberg (inorganic chemistry), Rolf Huisgen (organic chemistry, Wieland student, later on most quoted german chemist) and Feodor Lynen (biochemistry, he won the Nobel Prize in 1964) who also overtakes the management of the Max-Planck Institute for Cell Chemistry. Learn more
1954
1954-1959: Between Karlstraße and Sophiestraße four new institutes are built (organic, inorganic, physical chemistry and biochemistry). In addition, new buildings are being constructed there for the "Institute of Pharmacy and Food Chemistry" and the "Institute of Pharmaceutical Drug Science".
1964
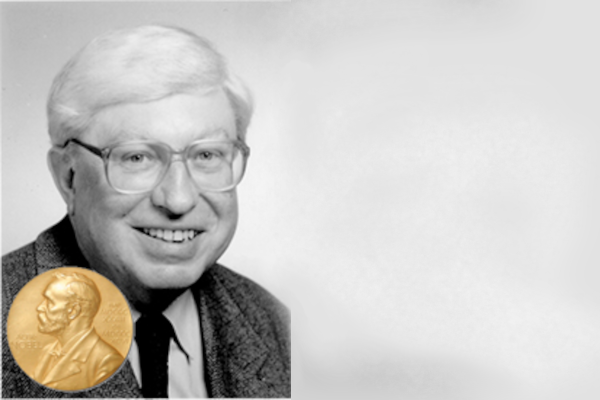
Feodor Lynen receives the Nobel Prize in Medicine
1973
Ernst Otto Fischer receives the Nobel Prize in Chemistry Ernst Otto Fischer was as professor part of the LMU Chemistry faculty from 1959-1964. Learn more
1999
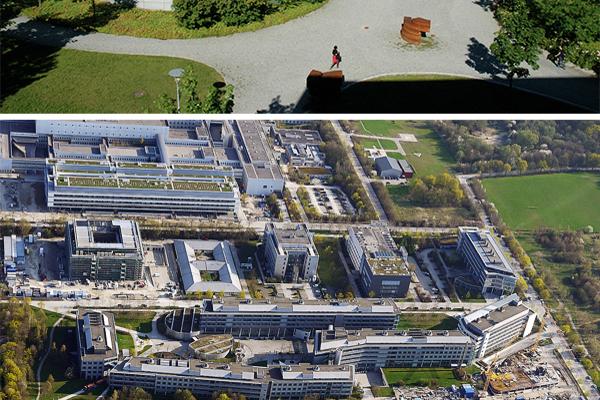
1999-2004: The faculty for chemistry and pharmacy moves to the "HighTech CampusLMU” at the western end of Munich. A Department for Chemistry and Biochemistry with the teaching fields anorganic, organic and physical chemistry and biochemistry is established. In addition, a Department for Pharmacy – Center for Pharmacy Research with the teaching fields pharmaceutical chemistry, pharmaceutical biology, pharmaceutical technology and biopharmacy as well as pharmacology for natural sciences is set up.
2007
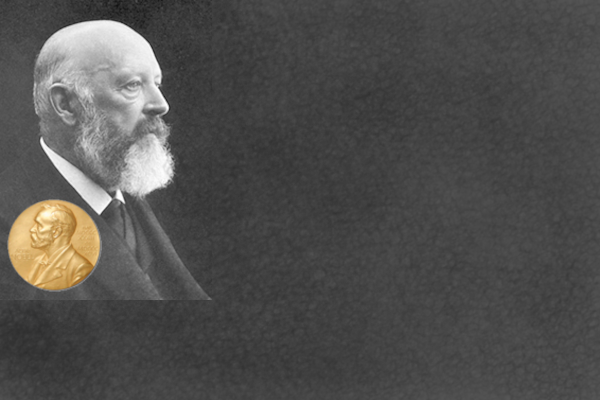
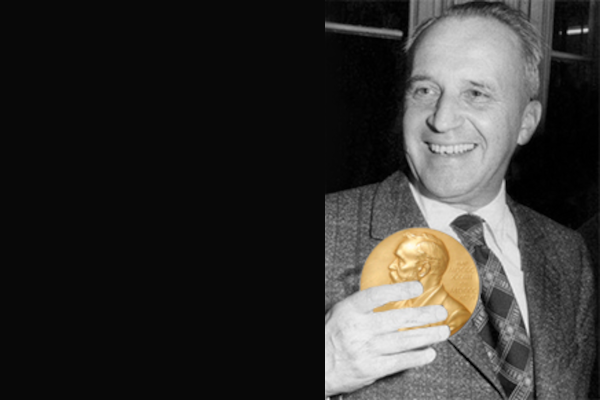
Chemistry Nobel Prize for Gerhard Ertl (1973 - 1986 member of the Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy of the LMU) Learn more
2016
Opening of the new research building "Center for Molecular Biosystems" BioSysM.
2021
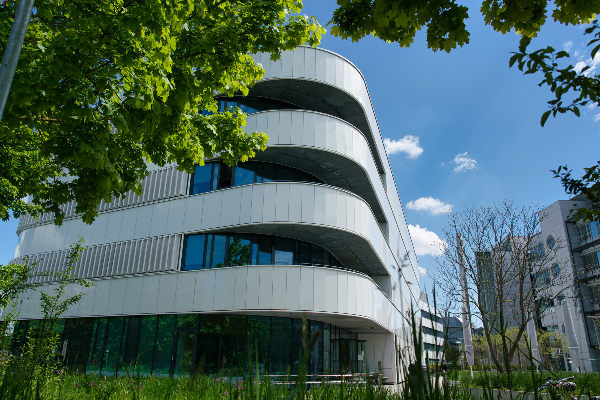
Opening of the new research building "Institute for Chemical Epigenetics" ICEM.